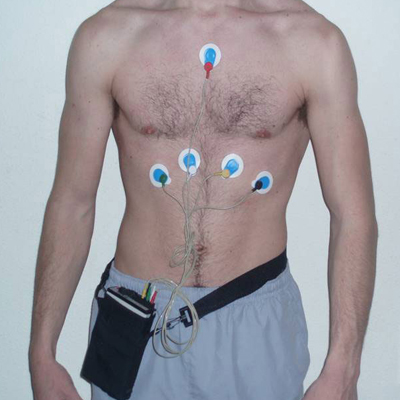
A Holter monitor is a small, wearable device that keeps track of your heart rhythm. Your doctor may want you to wear a Holter monitor for one to two days. During that time, the device records all of your heartbeats. A Holter monitor test is usually performed after a traditional test to check your heart rhythm (electrocardiogram), especially if the electrocardiogram doesn't give your doctor enough information about your heart's condition. Your doctor uses information captured on the Holter monitor to figure out if you have a heart rhythm problem. If standard Holter monitoring doesn't capture your irregular heartbeat, your doctor may suggest a wireless Holter monitor, which can work for weeks. While wearing a Holter monitor may be a little inconvenient, it's an important test that may help your doctor diagnose your condition. If you have signs or symptoms of a heart problem, such as an irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia) or unexplained fainting, your doctor may order a test called an electrocardiogram. An electrocardiogram is a brief, noninvasive test that uses electrodes taped to your chest to check your heart's rhythm. However, sometimes an electrocardiogram doesn't detect any irregularities in your heart rhythm because you're hooked up to the machine for only a short time. If your signs and symptoms suggest that an occasionally irregular heart rhythm may be causing your condition, your doctor may recommend that you wear a Holter monitor for a day or so. Over that time, the Holter monitor may be able to detect irregularities in your heart rhythm that an electrocardiogram couldn't detect. Your doctor may also order a Holter monitor if you have a heart condition that increases your risk of an abnormal heart rhythm. Your doctor may suggest you wear a Holter monitor for a day or two, even if you haven't had any symptoms of an abnormal heartbeat.